The cells of your body are always working to carry out complex tasks, most of which go completely unnoticed. But when there is a problem at the cellular level, the effects can be both serious and extensive. Enzymes are one of these small but critical components of healthy bodily function. They’re responsible for interacting with other chemicals inside the body to bring about certain reactions, such as converting complex sugars into usable energy. When there is a dysfunction with your enzymes, it can have harmful consequences that require lifelong treatments. Often, the best available course of action is simply to replace the deficient enzymes in a process known as enzyme replacement therapy. But what is enzyme replacement therapy and can it really help?
Enzyme Replacement Therapy: The Basics
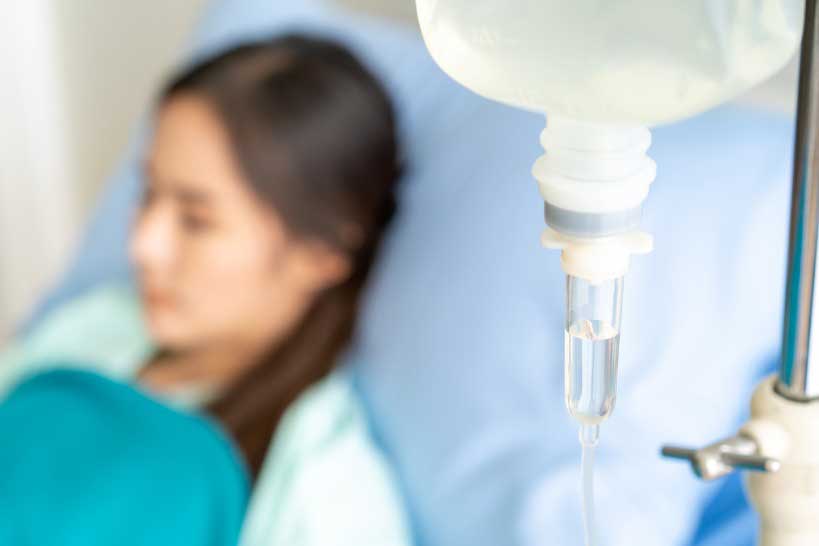
Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is a medical treatment whereby replacement enzymes are given to patients who suffer from chronic conditions resulting from enzyme deficiencies or malfunction. The most common method of ERT is through IV infusions, in which the replacement enzyme is administered directly into the bloodstream through a controlled drip of fluids. Replacement enzymes for ERT are derived from human, animal, and plant cells that are then genetically modified and processed before being given to the patient. By receiving these enzyme replacements, the body is able to successfully perform the functions inhibited by the deficiency. The effectiveness of ERT varies from person to person and what is being treated, but in some cases it is the only available treatment option.
Conditions Treated by Enzyme Replacement Therapy
The most common conditions treated by ERT are lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs). These rare, chronic, inherited diseases develop when enzymes are absent or malfunctioning inside the lysosomes. Lysosomes are what break down proteins and other macromolecules in the body, so when they are unable to do so, various symptoms and conditions develop, often with serious consequences on a person’s daily life.
Read: Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Lysosomal Diseases
Common LSDs treated with enzyme replacement therapy include:
Fabry Disease
Fabry disease occurs when the body is unable to make the enzyme necessary to break down a fat called globotriaosylceramide (Gb3 or GL-3). The lack of this enzyme, alpha-galactosidase A, causes buildup within the cells, which damages them and leads to serious symptoms throughout the body. Symptoms of Fabry disease include:
- Chronic episodes of pain, especially in the hands and feet
- Infrequent sweating
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Kidney failure
- Heart disease
- Dark red skin lesions – angiokeratomas, generally appearing between the abdomen and the knees
ERT for Fabry disease seeks to replace the deficient enzyme, alpha-galactosidase A. The two primary replacement enzymes used for Fabry disease are agalsidase alfa and agalsidase beta, which mimic the behavior of the enzyme they’re replacing. Infusions of these and other alternative ERTs must be given every two weeks, each infusion taking two hours to complete.
Read: Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Fabry Disease
Gaucher Disease
Gaucher disease occurs when there is a dysfunction of the glucocerebrosidase (GCase) enzyme, which is responsible for breaking down fatty chemicals in the body. A deficiency of GCase leads to a buildup of fatty cells known as Gaucher cells, in certain organs and in bone tissue. Symptoms of Gaucher disease include:
- Anemia and fatigue
- Abnormalities with bleeding and bruising
- Abdominal issues due to internal organ swelling
- Bone pain and other skeletal weakness
ERT for Gaucher disease involves replacing the deficient GCase enzyme with a genetically modified substitute, which allows the body to break down the fatty chemicals that would otherwise build up in the bones and organs. Infusions of enzyme replacements for Gaucher disease are given every 2 weeks, each session lasting between one and two hours.
Read: Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Gaucher Disease
Pompe Disease
Pompe disease develops from a deficiency of the enzyme alfa glucosidase (GAA), which is responsible for breaking down complex sugars (glycogen) in the body’s cells. In the absence of GAA, glycogen builds up in the cells, hindering them from getting the energy they need for proper function. This causes complications such as:
- Poor muscle development
- Trouble eating, breathing, and/or hearing
- Respiratory problems
- Enlarged liver and/or heart
- Problems with motor function
ERT for Pompe disease is the only effective treatment available today. Infusions of the deficient enzyme (GAA) or a genetically modified replica are administered into the body, allowing it to successfully turn glycogen into glucose (glycogenolysis). This process is what allows the body to properly use sugars and create energy at the cellular level. Like other lysosomal storage diseases, ERT treatments for Pompe disease must be given regularly in two-week intervals for the duration of the patient’s life in order to prevent the buildup of glycogen.
Read: Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Pompe Disease
Limitations and Side Effects of ERT
While in many cases ERT is the only effective treatment for a given lysosomal storage disorder, there are also some limitations and side effects to consider, such as:
- High cost of treatment. ERT treatments are expensive, with yearly costs in the hundreds of thousands of dollars. For most people this requires hefty assistance from insurance.
- Immunological response against the infused enzyme.ERT can trigger immune responses based on how the body reacts to the infused enzyme. These effects will vary from person to person.
- Development of resistance to enzymes. The effectiveness of some ERTs can decrease over time if the body develops a resistance to the replacement enzymes.
- Not a cure. Lifelong treatments are necessary with any ERT, sometimes even when adverse effects occur. While ERT can replace deficient enzymes, it does not produce in the body an ability to make them, so treatments must be given for the entire duration of a patient’s life in order to mitigate the effects of having a lysosomal storage disorder.
- Uneven biodistribution. This means that the replacement enzyme is not distributed the same across the entire body and its organs. Therefore, the effectiveness of the therapy may be limited in certain areas of the body, and some symptoms of the LSDs may persist despite therapy.
If Your Doctor Has Recommended Enzyme Replacement Therapy, Let Infusion Associates Help You
At Infusion Associates, we provide medically-prescribed infusion therapy for patients with chronic conditions in a welcoming and friendly environment. Our team of healthcare professionals is committed to making the experience as comfortable as possible. We always inform patients of any potential side effects and answer all their questions before starting treatment. In addition, we have a Registered Pharmacist on-staff to make the process as seamless as possible.
If you would like to refer a patient to us or want to inquire about the treatments we offer, you can contact us by calling us at 616-954-0600 or filling out this form.